When hazardous materials are involved, it is essential for occupant safety that building and fire codes are properly applied. Lead Fire Protection Engineer Robert Muellerleile brings clarity to the process of successfully incorporating these important codes into building design.
What are considered hazardous materials, and how are they classified?
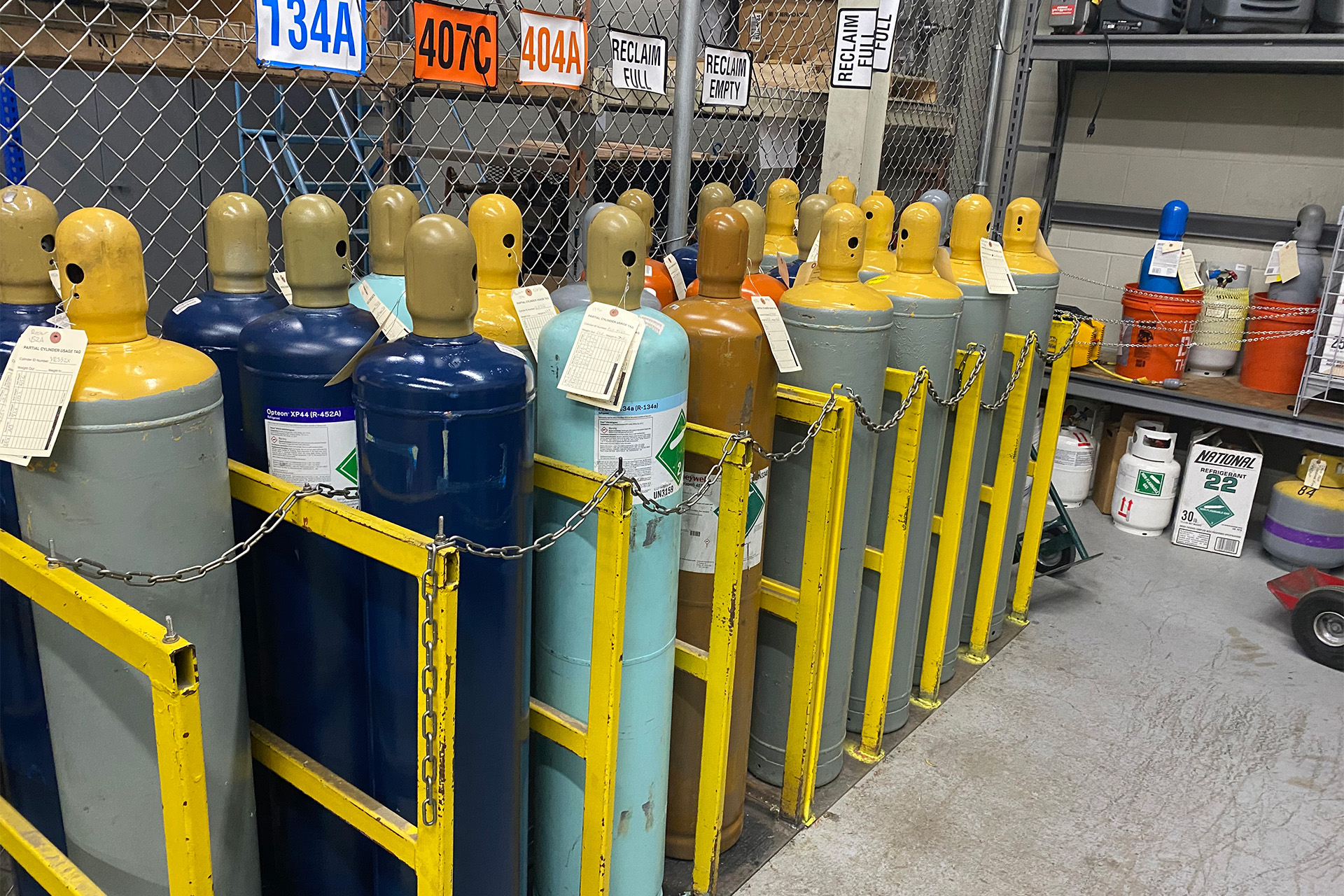
The building and fire codes define hazardous materials. They are materials that, by their use or physical properties, would be hazardous to people or structures. An example would be a flammable liquid, which would increase the rate of fire spread in the event of a fire or a toxic or corrosive chemical that presents a health hazard.
State fire code defines hazardous materials in various ways. For example, flammable liquids could be determined by their flash point and boiling point, and corrosives could be determined by the material’s reactivity.
What are the advantages of being proactive in managing hazardous materials?
Building owners who are proactive about managing operations and defining high-hazard occupancies have far more flexibility in their facility since it’s always harder to update to comply with building and fire codes retroactively. Building and fire codes limit the amount of each type of hazardous material in a facility to create safe environments. However, a facility may occasionally need more flexibility due to a process or to keep more inventory on site.

We work with building owners to find a solution unique to their facility. We may recommend constructing fire-rated walls to define a hazardous material control area, which allows a facility to increase the number of dangerous materials otherwise permitted in use or storage. Or, we may recommend creating a high-hazard or an H-occupancy space, which could allow a hazardous materials process that would otherwise exceed amounts permitted by the building or fire code. Lastly, we may recommend additional exhaust systems limiting the number of flammable vapors. By working proactively with our team, we can help find solutions to whatever the challenge.
What services can MCE provide related to managing hazardous materials?
Our team provides consultation in three mains steps:
- Classifying materials. We are proficient in analyzing Safety Data Sheets (SDS), reviewing the material’s physical properties, and defining how the fire code classifies them.
- Review processes. We visit our client’s facility to review how hazardous materials are stored, used, and dispensed. Or we review plans for a brand new facility in design.
- Determine solutions.Our team will recommend solutions, including defining control areas, high-hazard occupancies, and unique systems or processes to ensure a safe and code-compliant building.
What are the implications for fire protection systems in areas with hazardous materials?
Sprinkler protection for hazardous materials can be a highly complex analysis. We’re proficient in analyzing the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) standards to determine the appropriate type of sprinkler system needed based on the materials, their storage, and their use. In addition to sprinkler systems, we also design specialty fire suppression systems. For example, our team can determine if a foam or clean agent suppression system would suit a space. Given their materials and processes, we always focus on finding the right solution for our clients.